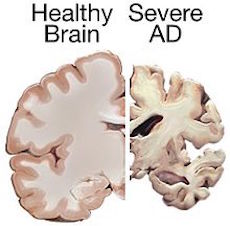
Gladstone researchers discovered that salsalate blocked the build-up of a protein that collects in Alzheimer’s patients’ brains. The study showed that the drug reversed cognitive decline and prevented the loss of brain tissue essential for memory.
The drug is considered fairly safe but is associated with the risk of heart attack and/or stroke in some patients.
Salsalate inhibits an enzyme in Alzheimer’s patients’ brains that makes tau toxic, prompting memory loss. Tau has been a focus of other Alzheimer’s research. Scientists don’t understand why tau builds up some brains or how it causes disease.
This is the first time that researchers have reversed the toxic aspects of the protein tau with a drug, said Li Gan, Ph.D., one of the senior researchers.
“Remarkably, the profound protective effects of salsalate were achieved even though it was administered after disease onset, indicating that it may be an effective treatment option,” Ms. Gan said.
The research was conducted on mice at the Gladstone Institutes. The animals had a rare form of dementia associated with Alzheimer’s.